Summary
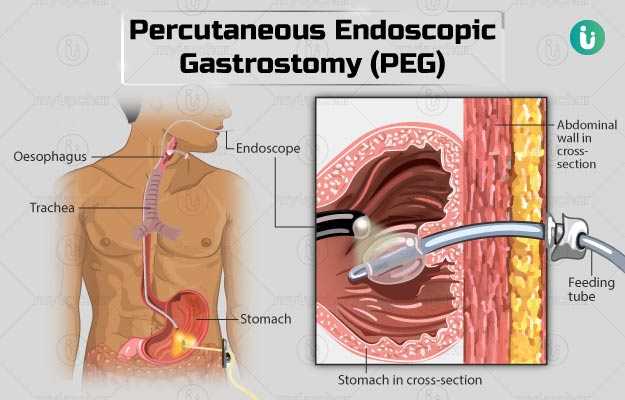
In percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy (PEG), a feeding tube is inserted into the stomach through a surgical opening in the abdomen. This procedure is recommended in individuals with conditions that cause difficulty in swallowing and complications related to it for example food going into lungs. A sedative will be administered during the procedure to help you relax, and local anaesthesia will be given to numb the area around the abdomen. The procedure takes about 20 minutes. However, you may need to stay in the hospital under observation for about three nights. Before you are discharged, a dietician will provide you with instructions on how to use and take care of your feeding tube. Like all other endoscopic surgeries, PEG is associated with a few risks or complications such as bleeding and infection.