Summary
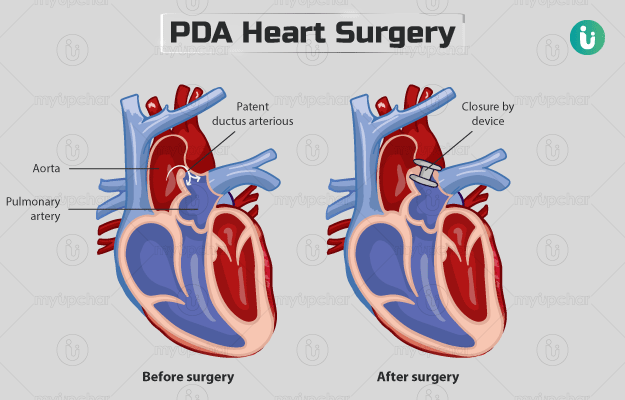
Patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) heart surgery is performed to treat a condition called Patent ductus arteriosus. Ductus arteriosus is a blood vessel between the pulmonary artery (a blood vessel that carries oxygen-poor blood to the lung from the heart) and aorta (carries oxygen-rich blood to the entire body from the heart) in a foetus (unborn baby). Generally, this duct closes after birth, however, in case it does not, the condition is called PDA. Smaller PDAs don't cause symptoms but larger ones lead to breathing difficulties and trouble feeding. PDA can continue into adulthood if it does not close on its own.
Various approaches, including medicine and catheterization, are used to treat PDA in newborns. Surgery is more commonly recommended in older infants and children when no other methods work.
You will be asked to fast before a PDA surgery. The procedure will be done under general anaesthesia. Once the surgery is done, the recovery may include medications to reduce infection and restriction on certain activities until you heal completely.