Summary
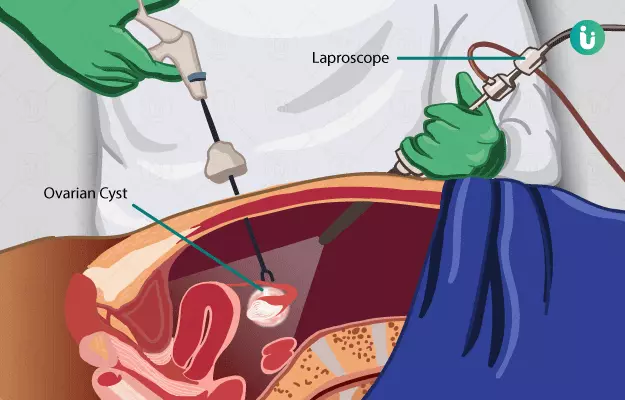
Ovaries are egg-producing reproductive organs that are usually present in a pair in the lower belly of women. In the process of releasing the egg from the ovaries, small cysts are formed every month, which disappear in a few weeks to months. However, some cysts may not dissolve on their own and persist for longer periods of time. These cysts may grow in size and cause symptoms like pain, weakness, bloating, and may even be cancerous. Some of these cysts may also cause rotation of the ovary, which can cut off its blood supply and cause its death. In such cases, removing the cyst by surgery is recommended. Around 7% of women worldwide have ovarian cysts at some point in their life. The surgery may be conducted in two ways - laparoscopy (less invasive and close surgery) and laparotomy (more invasive and open surgery).
Before surgery, you may have to undergo a few tests to ensure your fitness for surgery, such as blood tests, urine test, ultrasonography and so on. Once the cyst is removed, you will be discharged and few medications will be given to be taken on a regular basis for faster healing. A few complications may arise after surgery that includes fever, vomiting, vaginal bleeding, not being able to bear children, and so on. These risks, however, will be explained to you well in advance by your doctor.