Summary
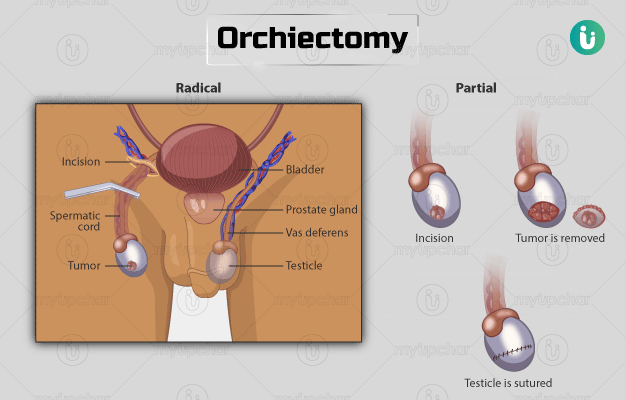
Orchiectomy is the surgical removal of either one or both testicles - male sex glands that are located behind the penis. It is commonly performed for treating testicular cancer but can also be done as a secondary procedure for prostate cancer treatment. to reduce the hormone (testosterone) levels and to avoid its recurrence. Testosterone promotes prostate cancer growth. Orchiectomy is also recommended as a part of gender change surgery.
In some cases, orchiectomy may be followed by another surgery to treat cancer that has spread to other parts of the body - abdominal lymph nodes for example. Therapies like chemotherapy and radiation therapy may also be recommended depending on the type of cancer.
After orchiectomy, reconstructive surgery with an artificial testicle may be advised to maintain the natural look of the genital. However, the decision is personal. The surgery may take about one hour and is performed under general anaesthesia. You may visit the doctor six weeks after the surgery.