Just before the procedure, you may be administered a sedative to help you relax. You will meet the surgeon and anaesthetist to discuss any additional doubts about the procedure.
After that, you will be administered either general anaesthesia which will keep you unconscious during the surgery or epidural or spinal anaesthesia in which you will be conscious but will not feel anything below the waist. The anaesthesia may be administered in the operation theatre or while you wait to be transferred into the operation theatre.
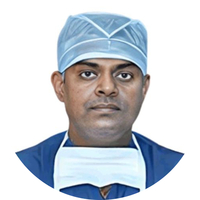
During the surgery, a doctor will replace the worn-out part with a prosthesis, which is a made-to-measure part of plastic or metal. This may be either a partial or total knee replacement depending upon the extent of knee damage.
The total knee replacement surgery takes about 1 to 3 hours, and both sides of the knee are replaced. The procedure is as follows:
- The surgeon will make an incision (cut) on your affected knee to expose the knee joint.
- They will remove the damaged parts, and appropriately measure and shape the ends so that the prosthetic fits.
- This will be tried by fitting a dummy joint to check the working of the joint, and then the final prosthetic is attached.
- The end of the thigh bone will be replaced with a curved metal prosthetic, and a flat metal plate will replace the end of shin bone.
- A special bone “cement” can be used to fix these to the bone or they can be treated with a coating to encourage the bone to fuse with the replaced parts.
- To reduce the friction, the surgeon will place a plastic spacer between the pieces of metal to act as cartilage.
- If required, the back of the kneecap may also be replaced.
- Once the procedure is done, the doctor will seal the wound using staples or stitches, and a dressing is done.
- Only in rare cases, a splint (a rigid or flexible material to protect an injured part) may be placed, but generally, movement of the knee is encouraged as early as possible.
A partial knee replacement is generally performed in about a quarter of the people with osteoarthritis. The surgery can be performed by a minimally invasive or reduced invasive technique. This is a relatively simple surgery in which a smaller incision is required and less bone is removed. The recovery period and hospital stay are also shorter with a partial knee replacement. Knee movement after a partial knee replacement is more natural, and you can lead a more active lifestyle compared to that after a total knee replacement. A blood transfusion is rarely required with this surgery.
You may experience some difficulty in bending and kneeling after a knee replacement surgery.
Immediately after the surgery, you will be taken to the recovery room and your vital signs (breathing, blood pressure and pulse) will be monitored. If required, you may be given oxygen through a tube or a mask. You may also be given a blood transfusion if needed. After you are alert and your vital signs are stable, you will be taken to your room (in the hospital) where you will have to stay for a few days.
Your knee will be covered in a dressing to protect the wound. A tube will be attached at the site of surgery to drain the blood and prevent it from collecting in the wound. Until the wound is healed, the dressing will be routinely changed. You will also have to take pain medications regularly.