Summary
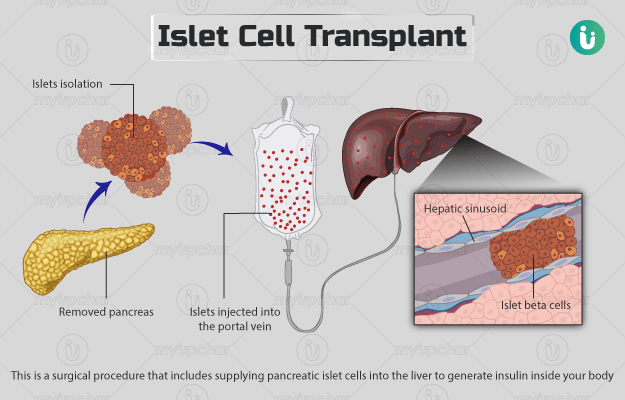
Islet cell transplantation is a surgical procedure that includes supplying pancreatic islet cells into the liver to generate insulin inside your body. Insulin is a hormone that helps maintain normal blood sugar levels. Islet cells are specialised cells inside the pancreas (a gland present in the abdomen) that produce insulin.
For this procedure, your surgeon may isolate islet cells from your pancreas (autotransplantation) or the pancreas of a deceased donor (allotransplantation). Allotransplantation is usually performed if a person's own islet cells have stopped the production of insulin (causing type 1 diabetes), whereas autotransplantation is conducted when a person's pancreas is removed (total pancreatectomy). You cannot drink or eat for several hours before this surgery. If you take insulin, your doctor will ask you to stop using it for a few hours before the procedure. Islet cell transplant is generally performed under local anaesthesia (numbs the surgical area). The surgeon may choose general anaesthesia (to keep you pain-free and relaxed) if the procedure is performed along with total pancreatectomy. The introduced islet cells may take six to 12 weeks to start generating insulin. Till then, you will be on insulin supplementation. You will be asked to check your blood sugar levels at least seven times a day at home until your follow-up visit. Also, the doctor may recommend certain restrictions on your diet and everyday activities to ensure good recovery.