Summary
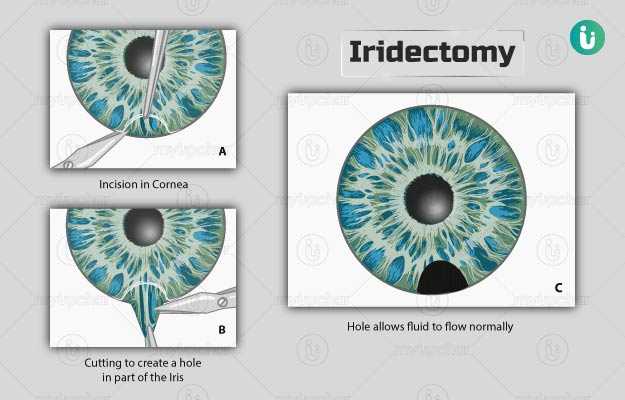
Iridectomy is performed to remove a small part of your iris either surgically or by laser (iridotomy). This surgery helps to reduce the increased pressure in the eye caused by certain conditions like melanoma of the iris or angle-closure glaucoma. The procedure is contraindicated in some instances such as if you have had multiple laser iridotomies in the past.
Before the surgery, the doctor will perform some tests, including tonometry and gonioscopy to assess your eye health. A laser iridotomy does not need much preparation; however, if you are undergoing a surgical iridectomy, you will need to fast for about eight hours before the procedure. You can return home on the same day and resume work from the next day of the surgery. To prevent any infections, your doctor will prescribe eye drops and ask you to wear an eye patch. A follow-up generally takes place after two weeks, but if you have any symptoms such as problems in your vision or if your pain worsens, consult your doctor immediately.