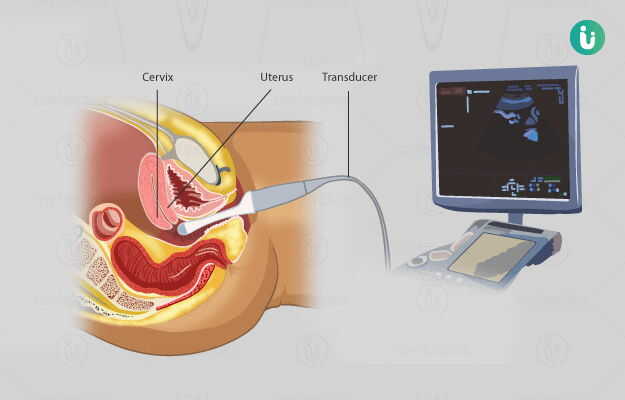
Hysteroscopy is a minimally-invasive surgical procedure used to internally visualise the cervix and the uterus (womb).
The procedure is done using a hysteroscope, which is inserted through the vagina and progressed up to the uterus. The procedure is used to assess and sometimes treat cervix and/or uterus related symptoms.
Prior investigations include blood tests and radiological tests. The procedure is often a daycare admission (the person is admitted in the morning and discharged by the evening).
Post-procedure, the aftercare is uneventful and the person can resume normal activities by end of the day.