The procedure is either done by a general surgeon or a paediatric surgeon depending on the age of the patient. The technique of the surgery along with the associated risks are explained to the patient/their parents or guardian.
A detailed medical history of the patient is taken which involves the symptoms, birth history (in case of babies), pre-existing conditions (comorbidities) if any and medications history. In babies, this history is given by the parents/guardian.
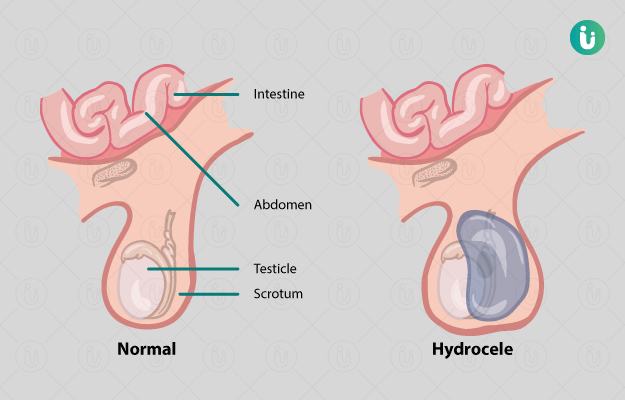
A physical examination of the patient is done to assess the hydrocele and rule out any other pathologies. Investigations that are done prior to the surgery include:
- Routine blood tests
- Chest X-ray
- ECG
- Ultrasound of the abdomen and ultrasound of the pelvis. This investigation is useful to:
- confirm the size of the hydrocele
- understand the type of fluid present within
- to identify any associated abnormalities (occasionally a part of the intestine may also be present – also known as an inguinal hernia). (Read more: Inguinal Hernia Surgery)
- visualise the other contents of the scrotum, including the blood supply to the testis
- assess the other testis and see whether it is normal
The surgery is done via day-care admission (the patient is admitted in the morning and discharged by the evening). The patient is advised to arrange for a ride back home since after the surgery, the patient will have difficulty driving.
Prior to the day of the surgery, the patient is told to fast overnight. For babies, fasting for at least four hours before surgery is required.
On the day of the surgery, the patient arrives at the hospital with all the relevant investigations and documents and is admitted. The patient is changed into the hospital attire and a final review of the patient is done by the surgeon and nurses before clearing for surgery.
Written consent is taken from the patient (or the parents/guardian in case the patient is a baby) after the surgeon has explained the technique of the surgery and the associated risks and complications. Hair, if present, is shaved off from the area of the surgery. Thereafter, the patient is shifted into the operation theatre (OT).