Summary
Joint replacements are one of the greatest success stories in the history of medical science. Among these, the total hip joint replacement is the most commonly performed procedure. The hip joint is one of the most important and biggest joints in the human body. It is a ball and socket joint and allows us to walk, run and jump. It is also the most flexible joint in the body after the shoulder joint. If the hip joint breaks in an accident or wears out with old age, then the person needs to get it replaced with ball and socket joint made up of metal or plastic which makes walking easier.
Hip replacement has transformed the lives of hundreds of thousands of people with arthritis (swelling in the joints) of the hip. Surgeons carefully choose people for a hip replacement who may have high chances of positive outcomes and use implants for long-term follow up. Most hip replacements will be uncomplicated and provide excellent results.
- What is a hip replacement surgery
- Why is hip replacement surgery done
- What preparations are needed before surgery
- How is hip replacement surgery done
- Self-care after hip replacement surgery
- What are the possible complications/risks of hip replacement surgery
- When to see your doctor
What is a hip replacement surgery
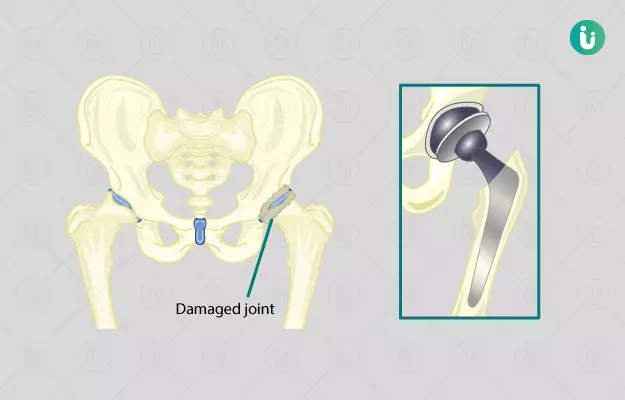
Hip replacement surgery is a procedure usually done by a surgeon to remove the painful hip joint when it gets fractured or damaged in an accident or induces pain while in resting position in old age and replaces it with an artificial one known as Prosthesis. Hip replacement surgery is a major surgery and only advised if other treatment options like medications, physiotherapy, and steroid injections have failed to reduce the pain.
Why is hip replacement surgery done
Hip replacement surgery is mostly done in the elderly, especially between 50-80 years of age. However, there are a few other conditions and factors in which hip replacement surgery is indicated. These are:
- Severe pain in the buttock and groin, which may also be present in or even below the knee.
- Functional disability or limitations of the hip joint.
- Pain that doesn’t subside by simple analgesics (pain killers) and causes regular loss of sleep.
- Stiffness in the hip area.
- Inability to walk for more than 400- 800m.
- A need to use walking aids, such as sticks or crutches.
- Difficulty in getting in and out of bed or chair, and going up or downstairs.
- Hip pain continues while resting throughout the day.
- Poor range of hip movement.
Common causes of pain in the hip joint include:
- Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is the inflammation or swelling in one or more joints due to cartilage degeneration. - Rheumatoid Arthritis
RA is a chronic (long-term) progressive/continuous disease that causes inflammation or swelling in the joints and resulting in their painful deformity and immobility. - A hip fracture
- Ankylosing Spondylitis
A long-term condition in which the spine and other areas of the body become inflamed or swollen. - Bone Dysplasias
A disorder characterised by abnormalities in bone and cartilage, such as abnormal shape, size and disproportional length of the bones. - Osteonecrosis or Avascular Necrosis
The death of bone cells/tissues. - Post-traumatic Arthritis
Inflammation/swelling of the joint which occurs due to physical injury. - Childhood hip disease
A condition wherein due to lack of blood flow, the bone cells die and bone stops growing.
What preparations are needed before surgery
Your orthopaedic surgeon will review the results of body tests and decide whether you need a total hip replacement to relieve your pain and restore function. The surgeon will always explain the risks or complications that may occur after surgery. Don’t ever hesitate to ask your doctor regarding anything which you don’t understand as the more you know, the better you will manage the outcome.
After your surgeon has given you the due date for your hip replacement surgery, the following things need to be done just before surgery so as to avoid any complications.
- Medical Evaluation
Your orthopaedic surgeon will ask you to get complete body tests done to ensure that you are healthy enough to undergo the surgical procedure and have a faster recovery. - Tests
Various tests, such as blood tests, urine test, ECG, X-rays, and so on are needed to plan the surgery to ensure its success without any complications. - Preparing your skin
Your skin should be free from any infections or irritations in the hip area. If it is present, consult your doctor before the surgery to get it treated. - Medications
It is crucial to tell your doctor regarding your regular medication and related health conditions, such as diabetes, high blood pressure, liver or kidney disease so that they can plan your medications and make necessary changes for the surgery accordingly. Otherwise, an avoidable situation may land you up in a more complicated situation due to side effects and adverse interaction of medicines. - Weight loss
If you are overweight then your doctor may ask you to lose some weight to minimise the stress over the artificial hip joint. - Dental evaluation
If any dental procedure is needed to be done then it must be completed before surgery, otherwise the chances of having an infection in your surgical area are increased as bacteria can reach the site through the bloodstream. - Urinary evaluation
As in old age, urinary infections are very common and frequent, an individual with a history of urinary infection should undergo complete urinary evaluation before the surgery.
How is hip replacement surgery done
On the day of surgery, you will most likely be admitted in the hospital for one day. After getting admitted, you will be evaluated to decide whether you need general anaesthesia (a procedure wherein medications that make you fall asleep during the procedure are given) or local anaesthesia/an epidural (where you are awake but you are numb from down the waist). The surgery usually takes a few hours to complete.
After this, your surgeon will decide the best prosthesis (an artificial hip joint or implant) for you. The implants have many different designs and materials like metal, plastic or ceramic. All the implants are made up of two basic components that are: a ball component (made up of highly polished strong metal material) and a socket component (a durable cup made of any one of materials like metal or ceramic or plastic).
- Conventional hip replacement surgery
In the conventional hip replacement, the surgeon makes a large cut of around 20-30 cm in the skin over the front and side of your hip and removes the diseased and damaged joint completely and replaces it with the artificial hip joint made up of the metal, ceramic or plastic. The upper part of the thigh bone (femur) is removed and the natural socket for the head of the femur is hollowed out in which the artificial socket is fitted. A short, angled metal shaft (the femoral stem) that attaches to your thigh bone, with a smooth ball on its upper end (the femoral head to fit into the socket) is placed into the hollow of the thigh bone. The cup and the stem may be pressed into place or fixed with acrylic cement - Minimally invasive hip replacement surgery
A new technique, called minimally invasive hip replacement uses a smaller cut of around 10 cm and a specially designed instrument is used to perform the surgery. It appears safe and effective like conventional treatment with one extra benefit of less postoperative pain.
After the surgery is done, you are moved to the recovery area for a few hours until you regain full consciousness. The medical staff will take care of your medications, will check your blood pressure, pulse rate and pain control from time to time.
Alternative to Hip replacement surgery: Hip resurfacing
In this, the femoral head is left in place but trimmed and capped with a metal covering. The damaged cartilage part is removed and replaced with a metal shell similar to the one in conventional hip replacement. It is predominantly considered for younger people. Hip resurfacing is less popular now due to the possible outcomes of damaging the soft tissue around the hips.
Advantages of hip resurfacing are:
- Bone conservation among younger people
- Improved range of motion and increased level of activity.
Self-care after hip replacement surgery
This is the period that demands your time and commitment to everything your surgeon instructed you to follow at home during the first few weeks of the surgery. These include:
- Wound care
The stitches over your skin will be removed approximately 2 weeks after the surgery. Avoid wetting the wound and put bandages properly. - Preventing blood clot formation
To prevent this, you need to sit up and try walking with crutches or walker as soon as possible after surgery. Stockings may be advised to compress the legs as it will help to prevent the blood from pooling in the leg veins and the chances of clot formation are reduced. Your surgeon may prescribe you oral or injectable blood thinners soon after the surgery. - Physical exercise
The physiotherapist may help you in speedy recovery with some exercises in the hospital, which you may also do at home. It is often recommended for strengthening the joint and muscles. - Diet
A proper diet with iron supplements is necessary for faster healing of the joint. Be sure to drink plenty of fluids. - Interior changes at home
Some changes might be necessary in the home environment including bed and chair raises, monkey pole attachments for the beds and handrails on the stairs, raised toilet seat, removing all loose carpets and electrical cords from the area where you walk to prevent accidental falls.
Another most important factor in having a successful hip replacement surgery is having realistic expectations. There is a significant alleviation of hip joint pain and improved daily life activities but excessive activity can speed up the normal wear of the artificial hip joint and may worsen your condition. Therefore, only realistic and practically possible activities are advised, such as low-impact activities which include walking, swimming, driving, and dancing. High-impact activities like running, jogging, jumping, lifting heavy weight should be strictly avoided. This way, hip replacement surgery will remain a great success and the artificial hip joint will last longer.
What are the possible complications/risks of hip replacement surgery
Mostly, hip replacement surgeries are successful and with least complications. However, there are a few risks/complications that you may face after surgery, such as:
- Hip dislocation where the artificial joint gives way.
- Infection at the site of the surgery.
- Injuries to the blood vessels or nerves.
- Blood clots.
- A fracture.
- Differences in leg lengths.
- Loosening and wearing off of the implant.
- Stiffness in the joint and legs.
When to see your doctor
Your doctor might call you in a week or two to remove your stitches and check for the healing of the wound. However, if at any point in time you observe the following symptoms, you should visit your doctor immediately:
- Excessive pain in the groin, hip or leg.
- Swelling at or near the hip joint that doesn't go away even after two weeks of surgery.
- A limp or problem in walking.
- Grinding from the hip.
- Chest pain or shortness of breath.
- Numbness, weakness, change in the vision or hearing.
- Fatigue.
- Feeling cold.
- Weight gain.
- Change in urination habits.
Surgery Cost In Your City
Doctors for Hip Replacement Surgery

Dr. Piyush Jain
General Surgery
5 Years of Experience

Dr. Rajive Gupta
General Surgery
28 Years of Experience

Dr. Prity Kumari
General Surgery
Dr. Mangesh Yadav
General Surgery
5 Years of Experience
References
- Crawford, R.W., Murray, D.W., 1997.Total hip replacement: indications for surgery and risk factors for failure. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 56, 455–457
- Ivory JP, Summerfield J, Thorne S, Lowdon IM, Williamson DM. Total hip replacement. Quality Health Care. 1994 Jun;3(2):114-9. PubMed PMID: 10137584
- National Health Scheme, United Kingdom. Hip Replacement Overview. NHS-Conditions. 2016 Oct 6
- National Health Scheme, United Kingdom. Hip Replacement: How it is performed. NHS-Conditions. 2016 Oct 6
- Gandhi R, Perruccio AV, Mahomed NN. Gandhi R, Perruccio AV, Mahomed NN. Surgical management of hip osteoarthritis. Canadian Medical Association Journal. 2014 Mar 18;186(5):347-55. PubMed PMID: 24144604