Summary
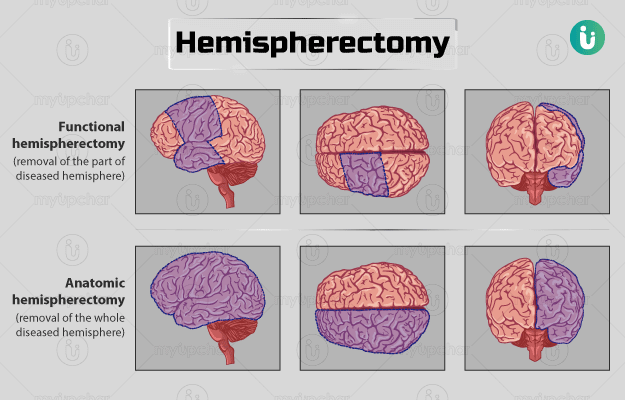
A hemispherectomy is a surgical method to remove or disconnect half of the brain - one hemisphere. Mostly, it is considered in people with severe seizure disorders originating from one side of the brain. Hemispherectomy is of two types – anatomical and functional. A thorough evaluation is done before the surgery to check if you are otherwise healthy enough for the procedure. These include necessary tests like EEG, Wada test and PET scan. The possible side effects of this surgery include speech problems, loss of movement and/or sensation on one side of the body.