Summary
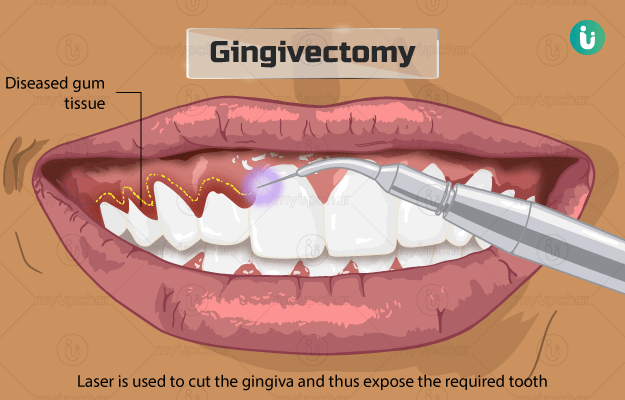
Gingivectomy is the surgical procedure used to incise the gums in the process of reshaping them for conditions such as periodontitis, gum enlargement, and gummy smiles. Gingivectomy should not be performed if there is any inflammation or if the pockets in the gums around the teeth are not too deep.
Before gingivectomy, the doctor will take your complete medical history, perform blood and radiological tests, and make you sign a consent form. They will also perform a cleaning procedure of your teeth and gums to prepare it for the surgery. The doctor will administer local anaesthesia before the procedure to numb the area. The surgery may be performed by scalpel, laser, or electrosurgery technique.
Once the anaesthesia wears off, you can resume your activities. You may take pain medication as prescribed to lower the discomfort. Eat soft foods and avoid hot drinks for a while after the surgery. You will have to visit the doctor for a follow-up after a week, but if you notice symptoms like nausea, fever, pain that lasts for a day after the surgery, contact your doctor immediately.