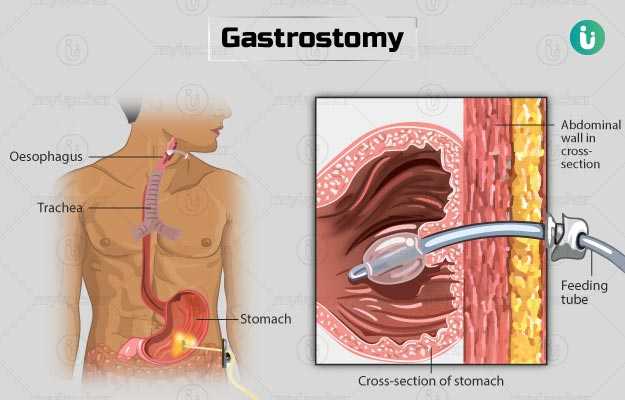
You will need to take the following care at home:
Wound care:
- Do not splash water on the wound for at least a few days after the surgery. only clean the skin around the surgical site gently. You can wash the area properly during a bath when your doctor allows you to.
- It is normal to experience some leakage from the incision site. You can clean the area with damp gauze.
Care of the tube:
Different types of gastrostomy tube need to be cared for differently. A nurse or your doctor will tell you how to care for the tube.
If the gastrostomy tube comes out accidentally, call your doctor immediately as the hole can close within a few hours. If you are given a spare tube to insert into the gastrostomy hole for such a condition, insert it in the opening quickly as explained by the doctor. This is because the gastrostomy opening closes quickly.
Taking medications through the tube: The tube can get blocked while taking tablets. So, if you have to take medicines for a health condition after the surgery, it is best that you tell your doctor about the tube so he can give you liquid medication.
If a tablet is still prescribed, then ground the tablet finely and mix with boiled water that should be cooled and then give it through the tube.
Additionally, flush the feeding device with water between each medicine delivery to prevent drug interaction and tube blockage.
Oral health:
- Brush your teeth twice regularly even if you do not eat or drink anything through the mouth.
- Use a water spray in the mouth if it feels dry.
Activities: You can swim once the surgical opening has healed. However, avoid indulging in contact sports as it can dislodge the device from its position. Discuss with the surgeon before making plans for travel.
Gastrostomy is a life-saving procedure and is often well-tolerated. It allows people to return to their daily activities.
When to see the doctor?
Call or visit the surgeon if you experience any of the following:
- Bleeding at the incision site
- Severe pain during delivery of medicines or feeding through the gastrostomy tube
- Leakage of stomach contents or feed from the incision site
- A dislodged tube
- Diarrhoea or vomiting
- Trouble emptying your bowels