Summary
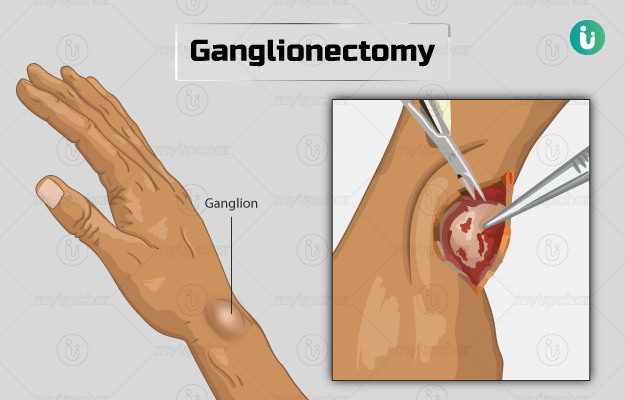
Ganglionectomy is the surgical removal of a fluid-filled sac called a ganglion cyst. A ganglion cyst usually originates from the joints or tendons and is commonly seen around the hand, wrist, nails or back of the foot. Surgeons recommend this procedure when the ganglion cyst restricts joint movement, making it difficult to perform normal activities. A ganglion cyst can also cause loss of sensation in its surrounding area.
Ganglionectomy is performed under general or local anaesthesia. It is done either by an open or keyhole method and is completed in 20 to 45 minutes. Your stay at the hospital thereafter depends on the type of anaesthesia used and your body’s reaction to it. It may take about six to eight weeks to recover from a ganglionectomy. You may need to visit the surgeon one to two weeks later to take out the stitches.