Summary
Our kidneys remove waste products and excess water from the blood. They also secrete hormones which control blood pressure and maintain the acid-base balance in the body. When these paired organs cannot perform their function properly, it can lead to the accumulation of waste products inside the body, which can be harmful. Dialysis is a treatment which can perform the function of kidneys by removing all the toxic wastes and excess water from the body. It is of two types - haemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis. In haemodialysis, the blood is drawn out with the help of two needles from the A-V fistula (the point where a vein and an artery are connected) to the dialysis machine outside the body, which filters the blood and sends it back into the body. In peritoneal dialysis, a catheter, which is a thin tube, is inserted inside the space covered by the membrane known as the peritoneal membrane in the stomach, the dialyser or dialysing fluid is inserted through the tube in which the waste products which are filtered from the blood are drawn. After dialysis, care should be taken about what you eat and drink. The diet should be planned by a dietician. There can be complications after dialysis like infection, weight gain, swelling, which can be taken care of with the help of medicines and surgery as per the advice of your doctor.
- What is a dialysis
- Why is dialysis done
- Preparations before dialysis
- How is dialysis done
- Post-dialysis care
- Risks and complications of dialysis
What is a dialysis
Kidneys are the most important organs of the urinary system. They are two in number, situated one on each side of your back, below the chest. The other parts of the urinary system include the ureters, which are two in number and connect the kidneys to the urinary bladder, where urine is stored inside the body. Healthy kidneys are the filters for removing waste products and excess water from your body and make urine. The kidneys also produce some important hormones inside your body, such as erythropoietin, calcitriol, and renin, which control your blood pressure, calcium absorption to make your bones healthy and strong, and in making the Red Blood Cells (RBC).
When your kidneys don't remain healthy due to various causes, they are not able to perform their functions properly. This leads to the accumulation of harmful waste products and an excess amount of water in the body. In such cases, dialysis is performed by which the excess amount of accumulated waste, water, and toxins can be removed from the blood.
Why is dialysis done
Kidneys filter excess waste in the form of urine. They also help in balancing salts and minerals in the body, such as calcium, phosphorus, sodium, and potassium. When kidneys are not able to perform their function properly, such as in kidney failure, it leads to the accumulation of these waste products and excess water in the body. This is when you need dialysis, which is also known as “renal replacement therapy”. Due to renal failure, the blood is not filtered, which can lead to serious health issues, such as anaemia, heart diseases, high blood pressure, and a disturbed pattern of absorption of different minerals that ultimately affects the bones.
There can be different kidney diseases, such as acute (a disease that progresses rapidly) and chronic (long-term and slowly progressing diseases), which when not treated properly can lead to kidney failure. Dialysis can help in protecting kidneys from failure. The kidneys can get back to normal after completion of the treatment for acute kidney disease. Once that happens, dialysis can be stopped. However, in the case of end-stage and chronic kidney diseases, recovery is hardly achievable and dialysis might be the only way left.
Preparations before dialysis
Before dialysis starts, there is a small surgery performed by the surgeon depending upon the type of dialysis you would undergo.
Dialysis is of two types:
- Haemodialysis
In haemodialysis, an A-V fistula (a point of connection between an artery and a vein) is created surgically. - Peritoneal dialysis
In peritoneal dialysis, a catheter (a long germ-free tube) is inserted surgically in the space between the membrane covering the stomach organs and the stomach wall.
Before undergoing surgery, you might need to undergo a few tests as described below:
- The tests to be done before surgery
Before the surgery is done, there are many tests which your doctor may suggest, such as an X-Ray, Electrocardiogram (ECG), Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), Complete Blood Count (CBC), urine test and tests related to the kidneys. Testing for HIV, Hepatitis C may also be advised by your doctor. - Testing of the numbing agent before surgery
The selection of the numbing agent depends upon the type of surgery. Numbing agents are given before surgery so you don’t feel the pain while getting operated. You may be advised not to eat anything at least 6-12 hours before surgery because it can lead to the backflow of food into the windpipe.
Things you should know before going for surgery:
- You should speak with your doctor about planning the surgery before dialysis. Your doctor will tell you the risks and complications which may be associated with the surgery. You will also get to know how the surgery will help your dialysis treatment.
- You should tell your doctor about your medical history, such as any medications that you’re taking, especially blood thinners or if you have undergone any surgeries in the past, such as a Caesarian-section.
- Inform your doctor if you consume alcohol, or tobacco on a regular basis.
- Take the medication as prescribed by your doctor before surgery, such as an antacid to neutralise the effects of excess acid production in the stomach, antibiotics to prevent or manage infections and painkillers to reduce pain before surgery.
- On the day of the surgery, blood pressure, temperature, blood tests, and airway will be checked before preparing you for the surgery.
- You will be asked to wear a germ-free surgical gown. During surgery, you will be covered with a germ-free cloth and only the area where the surgery is to be performed will be exposed.
- Someone from the family or close friends should accompany you to the hospital on the day of surgery.
- Stay stress-free, both physically as well as mentally.
- You should not smoke or drink alcohol before surgery as it will decrease the rate of recovery.
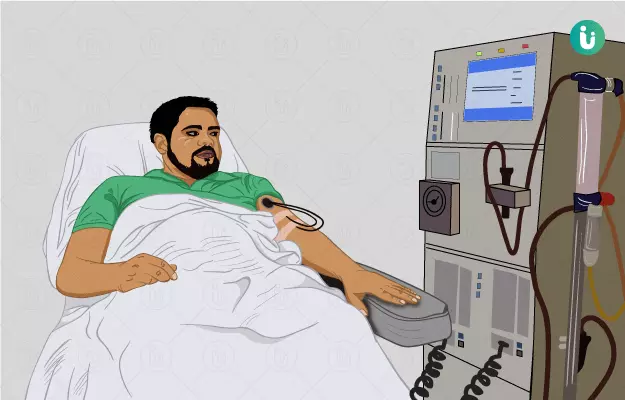
How is dialysis done
Haemodialysis
It is a method by which the blood is filtered such that the waste products and excess water in the blood are removed. The procedure is discussed below:
- In this treatment, the blood is drawn out of the body to a filter which is known as a dialyser.
- Before starting the treatment, the nurse puts two needles into your arm at the A-V Fistula, the point where an artery and a vein are connected. It is created by the surgeon before putting you on dialysis.
- The area is numbed by using a cream or spray containing a numbing agent.
- One needle is put in the artery from which the arterial blood is drawn out and the second needle is placed in the vein from where the filtered blood goes inside the body.
- Both the needles are connected to a tube which is soft and thin. It takes the blood to the dialysis machine outside the body.
- The dialysis machine then filters the blood by passing it to the filter. The filter has thin, hollow fibres, which separate the waste products and excess water from the blood.
- The filter also has a dialysing solution. The waste products move into this dialysing solution as it passes in the opposite direction of the flow of blood in the tubes.
- The dialysis machine also has blood pressure monitors installed at intervals. They measure your blood pressure as the blood is passing through the tubes.
- The process is mostly painless but sometimes you may feel nauseated and sick.
- Due to the rapid change in the blood constituents, there can be cramps in the muscles after dialysis. It can be done at home once you get well-trained by a nurse or doctor and learn how to put the needle inside the A-V Fistula.
- Small dialysis machines are available for home use. They allow you to have frequent dialysis sessions at home. It is mostly done three times a week.
Peritoneal dialysis
It is a treatment by which the blood is filtered by removing the toxic wastes and excess water, the function which healthy kidneys used to perform. In this type of dialysis, the blood is filtered inside the body by passing it through the natural membrane of the body known as peritoneum. The peritoneum lines the space between the inner abdominal wall and covers different organs in the belly, such as liver, kidney, spleen and intestines. The peritoneum has a rich supply of blood.
Peritoneal dialysis is of the following two types:
- Continuous Ambulatory Peritoneal dialysis (CAPD)
- Automated Peritoneal Dialysis (APD)
Preparation before peritoneal dialysis
Surgically, a 0.5 cm wide thin tube that is known as a catheter is inserted in the space covered by the lining. A small part of the thin tube is kept out of the body, which is connected to two different bags. One bag contains a special fluid which is pushed through the tube and then the waste products diffuse from the blood into this special fluid. This fluid is then drawn out of the tube into another bag, which collects the waste products. This whole process of fluid in and out of the body is known as an exchange. The bags need to be changed after every exchange.
Continuous Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis (CAPD)
In this type of peritoneal dialysis, the blood is filtered many times, mostly four times a day. The whole process takes around 30 minutes and can be done at home once you get trained in performing the dialysis yourself. Between every exchange, you can do your normal activities. You can have the four exchanges at different timings in a day, such as one in the morning, afternoon, evening and the last one at night. After every exchange, the bags are to be removed and the tube should be sealed properly.
Automated peritoneal dialysis (APD)
In this type of peritoneal dialysis, the blood is filtered all night when you are sleeping. It takes around 8-10 hours for this process. A machine is attached to the thin tube inserted in the peritoneal space. When you are sleeping, many exchanges happen all night - usually three to five. A fluid known as dialysate is placed inside in which the waste products diffuse. Later on, this fluid is drawn out of the body.
The cost of dialysis for a month is around 30,000 depends upon the hospital. Some may provide home dialysis which is cheaper for around 20,000 a month.
Post-dialysis care
- The most important aspect that you need to take care of after dialysis is your diet. It is crucial that you know what and how much you should eat and drink.
- The kind of diet you need to take depends on the kind of treatment you are going through. Discuss a diet plan with a dietician who would tell you about the right amount and type of nutrients you need to include in your meals.
- A good and balanced diet can replace much of the nutrients which are lost during the treatment. However, care should be taken not to include too much of the nutrients. This is because excess nutrients may get accumulated in the body as your kidneys have lost their normal function.
- The amount of water intake should also be taken care of. There can be an accumulation of excess water inside the body which can lead to high blood pressure, swelling and so on.
- The intake of salt should also be restricted in the diet.
- The food rich in minerals like potassium and phosphorus, such as meat, fish, beans and dairy products like milk and curd should be reduced.
Risks and complications of dialysis
Complications of Haemodialysis
A few complications that may arise because of haemodialysis include:
- Infections
- Muscle cramps
- Low blood pressure
- Fluid overload
- Hyperkalemia (increased potassium levels in the blood)
- Reaction to the dialyser (the fluid that is used for dialysis)
- Itchy skin
- Difficulty in sleeping
- Anxiety
- Dry mouth
The above-mentioned risks should be discussed with your doctor for their respective treatment and management.
Complications of Peritoneal dialysis
- Peritonitis
It is the inflammation (swelling) of the peritoneum, the lining of the stomach wall. Peritonitis can happen if the instruments used during peritoneal dialysis are not germ-free. It can be treated by antibiotics (to kill the germs) and anti-inflammatory medicines (to reduce the swelling) prescribed by your doctor. - Weight gain.
- Exit site infection.
- Catheter malfunction (the tube inserted in the peritoneal space).
- Intra-abdominal adhesions (scar tissue formation between the inner lining of the belly and the lining that covers the belly organs).
- Excess growth or lump can be seen in the stomach due to the presence of fluid in the tube for a longer time leading to stretching of the muscles of the stomach.
Surgery Cost In Your City
References
- Victoria State Government. Kidneys - dialysis and transplant. Better Health Channel. Conditions and Treatment. 2017 Jul.
- U.S. National Library of Medicine. Dialysis. NIH. MedlinePlus.
- Centre for Disease Control and prevention. Guidelines, Recommendations and Resources: Dialysis Safety. Dialysis Safety. 2017 Nov 17.
- U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. Your Kidneys & How They Work. 2018 Jun. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases.
- Health Direct. Dialysis. Australia. 2018 Feb.
- Zambouri A. Preoperative evaluation and preparation for anesthesia and surgery. Hippokratia. 2007;11(1):13–21.
- U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. Hemodialysis. 2018 Jan. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases.
- U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. Eating Right with Kidney Failure. 2018 Jan. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases.
- Jameson MD, Wiegmann TB. Principles, uses, and complications of hemodialysis. The Medical Clinics of North America. PMID: 2195264
- Alwakeel JS, Alsuwaida A, Askar A, Memon N, Usama S, Alghonaim M, Feraz NA, Shah IH, Wilson H. Outcome and complications in peritoneal dialysis patients: a five-year single center experience. 2011 Mar. Saudi journal of kidney diseases and transplantation. PMID: 21422621
- Shusterman NH, et al. Management of refractory peritonitis to maintain the peritoneum for subsequent dialysis. 1992. Journal of the International Society for Peritoneal Dialysis. Vol.12 no. 2 211-213. PMID 1586682
- Bares C. Follow up of patients in chronic haemodialysis. Acta psiquiátrica y psicológica de América latina. PMID: 547684