Summary
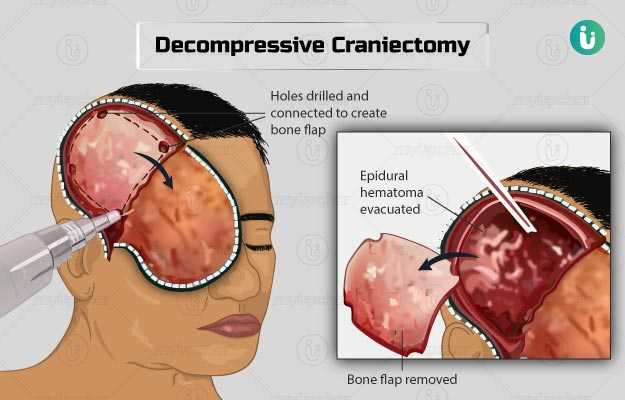
Decompressive craniectomy is performed to relieve pressure on the brain resulting from a brain swelling that is caused by an injury or other conditions. The procedure involves the removal of a part of the skull to allow space for the swelling to grow upwards. You will remain asleep during the whole procedure. The part of the skull removed during the surgery will be replaced a few months after recovery. In some cases, a synthetic skull is placed instead of the original part of the skull. Your stay at the hospital depends on the extent of injury to the brain. This surgery is associated with a longer recovery period, which could be anywhere from a few months to years. You may also be required to undergo rehabilitation for complete recovery from the surgery.