Summary
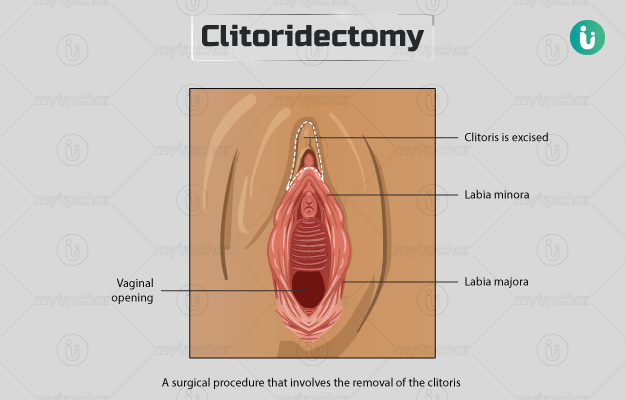
Clitoris is a small, sensitive structure of the external genitalia in women. It is comparable to the male penis and is responsible for pleasure during sexual activity. It is located at the upper junction of the inner vaginal lips and is protected within the outer lips of the vagina. Clitoridectomy is the removal of the entire clitoris. This surgery is done for the treatment of reproductive cancers (mostly invasive cancers) and if there is enlargement or necrosis (death of the tissue) of the clitoris. The surgery involves clamping and removal of the clitoris. Some complications associated with clitoridectomy include pain, reduced sexual appetite and libido, bleeding from the incision and urinary tract infections.
Clitoridectomy is also performed as a part of female genital mutilation (FGM) in some regions of the world. The World Health Organization advocates against any kind of FGM procedures.