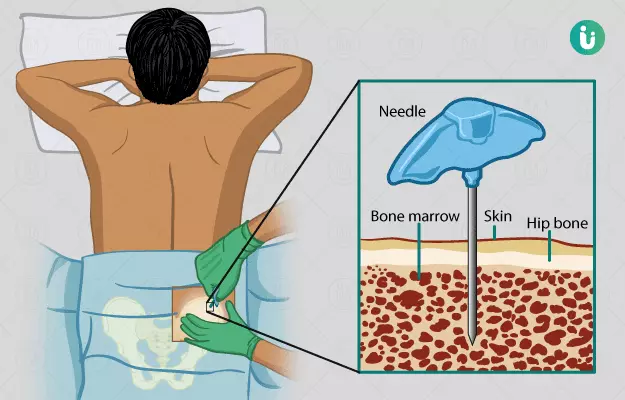
Bone marrow is a spongy substance in the centre of some of our bones (medullary cavity) that is a reservoir for stem cells. Bone marrow transplant is a procedure to replace damaged or destroyed bone marrow stem cells with healthy bone marrow stem cells.
Stem cells are capable of generating red blood cells which help in blood formation, white blood cells which fight infection, and platelets which help in the clotting of blood after an injury.
Different types of blood cancer and aplastic anaemia are just some of the conditions in which medical practitioners recommend a bone marrow transplant. Doctors perform tests like the bone marrow aspirate examination to confirm or rule out the presence of diseases which may necessitate a bone marrow transplant.
For a bone marrow transplant, the healthy stem cells are extracted, either from the patient’s own body or from a donor, and filtered before being transplanted into the recipient. Bone marrow found in the hip and the spine are the richest sources of bone marrow cells, though stem cells are taken from the blood circulating in the body in 90% of transplants.
When the procedure is successful, the transplanted stem cells grow and become new and healthy bone marrow. The transplanted stem cells are called a graft.