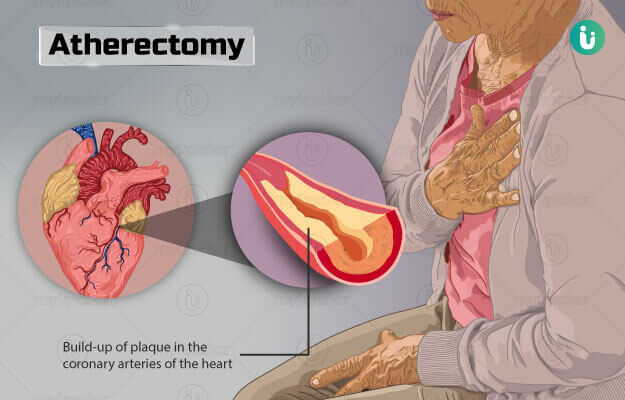
Atherectomy is a minimally invasive, interventional management that is used to remove atheroma (plaque) from arteries. It is undertaken for patients who have narrowed arteries due to plaque build-up that results in symptoms of distress.
Investigations include routine blood tests and a few special radiological tests. Although the procedure is short in duration, it requires a prolonged observation. Hence, the patient may require a hospital stay for a couple of days.
There is minimal risk in the procedure and provides good results.
- What is atherectomy
- Indications for the procedure
- Contraindications for the procedure
- Preparations before the procedure
- What happens during the procedure
- Risks and complications of the procedure
- Aftercare discharge and follow up
- Takeaway
What is atherectomy
Plaque is an abnormal build-up of fat within the walls of the artery which results in the narrowing of the lumen of the artery. As a result, blood flow through the artery decreases. This leads to hypoxia - a condition where there is an insufficient oxygen supply to various parts of the body, which can cause symptoms of distress, the most common being pain.
Removal of the plaque becomes necessary to alleviate the symptoms. Atherectomy is a minimally invasive, interventional procedure used to remove an atheroma (plaque). The plaque is removed by inserting a special catheter (thin tube) with specific tools at its tip which help remove the plaque.
Indications for the procedure
Atherectomy is indicated in the following conditions:
- Coronary artery disease: in patients whose coronary arteries (arteries that give blood supply to the heart) are narrowed or clogged due to plaques, especially when the plaque is quite hard to dissolve. Significant blockage can produce symptoms of a heart attack which include:
- Chest pain
- Pain radiating to the left arm, back and jaw
- Excessive sweating
- An impending sense of doom
- Peripheral heart disease: in patients whose peripheral arteries are narrowed (i.e. the arteries of the limbs, especially the legs). A significant blockage will produce symptoms such as:
- Cramping pain in the legs, especially after activities such as walking or running (claudication pain), which is not relieved by elevating the legs. Pain progresses and will be present even while resting – also known as rest pain
- Numbness or weakness in the legs
- Bluish discolouration of the legs, starting from the extremities and progressing upwards
- Sores that do not heal
- Reduced hair growth and toenail growth
- The skin over the legs becomes shiny
- Patients in whom despite having an angioplasty, the plaque has recurred
Contraindications for the procedure
The risk of performing the procedure increases if any of the following is/are present:
- Uncontrolled blood pressure
- Uncontrolled blood sugar
- Coagulopathy (excessive bleeding or clotting)
- Pregnancy
- Kidney dysfunction
- Severe anaemia
- Pre-existing heart conditions such as irregular heartbeat or a weak heart, if atherectomy is being done for cardiac arteries
- Active systemic infection
Preparations before the procedure
The procedure is usually done by a vascular surgeon. The surgeon explains the procedure along with the outcome and associated risks.
A detailed medical history of the patient is taken, which includes the patient's symptoms, family history, menstrual history (if applicable), medical history (if any other pre-existing illnesses are present), medications history, history of any substance use (alcohol or smoking), history of any allergies to food, etc. This is accompanied by a physical examination of the patient.
Certain other investigations are done that include:
- Routine blood tests
- Coagulation tests
- Kidney function tests
- ECG, Cardiac ECHO
- Chest X-ray
- Angiography (special radiological investigations which identify blocked blood vessels) of the vessel that is to be treated using a radioactive dye.
Medications, if any, for any pre-existing conditions may be altered or stopped as per the surgeon's orders.
Although the surgery is short in duration, it requires two to three days of hospital stay. The patient is told to arrive a day prior to the procedure, with all the relevant reports and documents to get admitted. Once admitted, they change into hospital attire.
Instructions before the procedure include:
- Shaving the hair over the area where the procedure will be performed
- A sedative may be prescribed to the patient, to be taken before sleeping to reduce anxiety related to the procedure
- The patient is required to fast after midnight
- Medications, as prescribed by the doctor, will be continued unless told otherwise
On the day of the procedure, a final review of the patient is done by the surgeon and the nurses before the patient is shifted for the procedure.
What happens during the procedure
The patient is shifted into a procedure room called the Cath lab. The patient is made to lie flat on their back on an X-ray table. A monitor is attached to track the patient's vitals (heart rate, blood pressure, oxygen saturation). An IV cannula is inserted through which medications required for the procedure are given.
The patient will remain awake throughout the procedure. To prevent pain, a mild anaesthetic is administered. Sterile (clean) drapes are placed on the groin followed by an incision using a scalpel (thin sterile blade) and the catheter is then inserted. A local anaesthetic may be given before the incision to minimise the pain.
Once the catheter is placed, it is slowly passed along the lumen of the blood vessel towards the area of blockage. The patient does not feel the catheter moving through the blood vessel since it has fewer nerve fibres. The progression of the catheter is monitored through serial dynamic X-rays.
Once the catheter is at the desired position, the plaque is removed using special tools present at the tip of the catheter. Based on the tools attached to the tip, any of the following techniques can be performed:
- Directional atherectomy: the tip of the catheter has a sharp tiny blade that shaves pieces of the plaque gently and transfers them into a pouch in the catheter. This technique is only advised in arteries of the limbs and is contraindicated in arteries supplying major organs such as kidneys or the heart. The surgeon may need to pass the catheter multiple times to remove a significant amount of plaque.
- Rotational atherectomy: the cutting tip of the catheter spins at high speed and drills through the plaque. The resulting plaque powder is easily washed away via the bloodstream.
- Laser atherectomy: the tip of the catheter contains a device that produces a high energy laser beam that vaporises the plaque.
- Orbital atherectomy: this is a more modern and more efficacious method, similar to rotational atherectomy, but the catheter tip has some extra modifications.
Based on the expertise of the surgeon, one of the above techniques is used to get rid of the plaque. Once the plaque is removed, a special radio-opaque dye is injected to see the blood flow through the treated vessel. Additional interventional procedures, if required, may also be done.
Once the plaque is dealt with, the catheter is slowly pulled out from the incision site completely. A pressure bandage is then applied to the incision area to stop the bleeding. The entire procedure usually takes about two hours.
Risks and complications of the procedure
Risks associated with the procedure are minimal. However, some of the risks are:
- Embolisation of the plaque: dislodgement of a large piece of the plaque that may block other vessels
- Perforation of the blood vessels
- Allergy to the dye can cause symptoms such as:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Drop-in blood pressure
- Fast or slow heart rate
- Itching with rashes over the body
- Infection
- Air embolism (introduction of air into the blood vessel)
- Recurrence of the blockage, especially in patients who continue to smoke cigarettes (cigarette smoking is a causative factor for peripheral artery disease)
Aftercare discharge and follow up
After the procedure is complete, the patient is shifted into an observation room. To prevent rebleeding, the patient is made to lie down for a few hours and instructed not to sit up suddenly, stand or raise their head. Pain is managed by analgesics. IV fluids may be administered; however, the patient is advised to start oral fluids as soon as they can.
The patient is kept under observation for one or two days before they are discharged. During the observation, notify the doctor immediately if any of the following symptoms are noticed:
- Extreme pain at the incision site
- Bleeding at the incision site
- Tingling or numbness in the legs or toes
- Chest pain, difficulty in breathing, dizziness, vomiting
Redness (rash) or mild swelling is common at the incision site and subsides over a few days. In case the swelling increases, notify the doctor immediately.
A discharge summary is prepared by the surgeon which includes relevant medications and advice on wound care. These typically include:
- Continuation of medications for pre-existing conditions, if any
- Antibiotics and analgesics to prevent infection and pain, respectively
- Post-surgery swelling and pain will be there for 12 to 24 hours and thereafter reduces as the days progress
- Strenuous activities such as lifting weights, running, etc. should be avoided for at least a week
- Advice on certain lifestyle changes that include diet and exercise to facilitate recovery and prevent recurrence of the plaque
- Reduction/cessation of alcohol and cigarette consumption is advised to prevent a recurrence
The first follow up occurs usually within a week and, thereafter, is as per the requirement of the patient.
Takeaway
Atherectomy is a minimally invasive interventional procedure that manages to alleviate the symptoms of the patient quickly and definitively. The procedure is of short duration with minimal risks and good results. It can be combined with adjuvant interventional procedures and can be used as an alternative to angioplasty if the latter is not possible or proves unsuccessful. The hospital stay is of a couple of days and aftercare is usually uneventful. With proper lifestyle modification, the recurrence of the plaques is drastically reduced thereby increasing the quality of life.
Surgery Cost In Your City
Doctors for Atherectomy

Dr. Manju
Cardiology
10 Years of Experience

Dr. Farhan Shikoh
Cardiology
11 Years of Experience

Dr. Amit Singh
Cardiology
10 Years of Experience