Summary
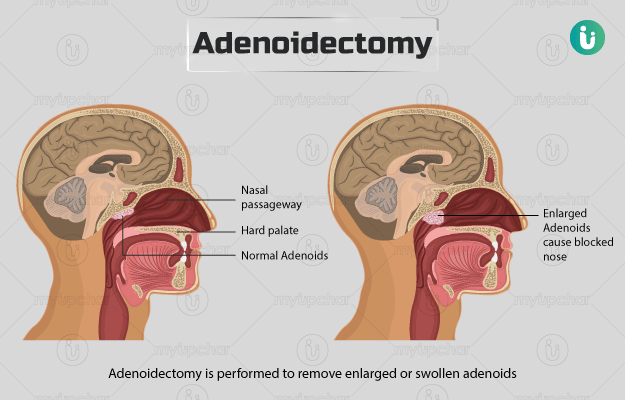
Adenoidectomy is performed to remove enlarged or swollen adenoids, which are lumps of tissue located behind the nose. Normally, adenoids help fight off infections caused by bacteria and viruses, however, if they become enlarged, they will obstruct the airway, making it difficult for a person to breathe through the nose. Enlarged adenoids also cause ear infections and difficulty in sleeping at night. Therefore, adenoidectomy is usually advised for these conditions. Enlarged adenoids occur typically only in children as adenoids shrink away in adulthood. The surgery is generally performed under general anaesthesia, which puts the child to sleep during surgery. The operation takes about 30 minutes, and the child is often discharged after a few hours. It takes around two weeks for the child to recover from the surgery completely.