What is strep throat?
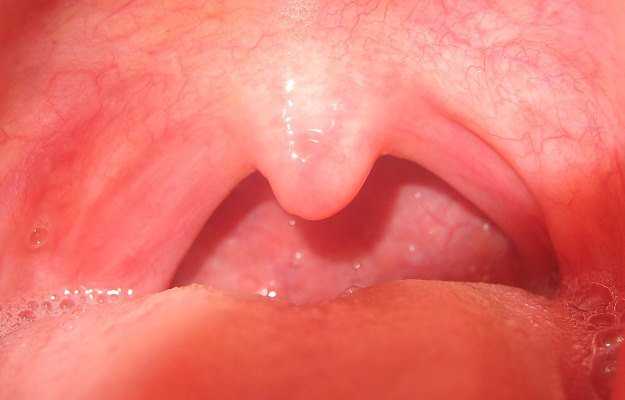
Strep throat is an infection caused by the Streptococcus pyogenes bacteria, which leads to pain, inflammation and discomfort of the throat. Although it can affect people of any age, it is more common in children.
What are its main signs and symptoms?
- Strep throat begins with soreness and discomfort in the throat that is particularly aggravated during swallowing or eating, and there is marked itchiness accompanying it; however, there is no cough.
- The tonsils are swollen and red with enlarged lymph nodes in the neck.
- Fever and chills develop as a result of this infection.
- A person may develop fatigue, headache and cold.
- Loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting are some other common complaints seen in those with a strep throat.
What are the main causes?
- Strep throat is caused by a bacteria belonging to Group A Streptococcus, Streptococcus pyogenes.
- This infection is transmitted from person to person through droplets released on coughing or sneezing.
- Close contact with an infected person also puts you at the risk of getting strep throat. This means touching or sharing personal items.
How is it diagnosed and treated?
- Strep infections have similar manifestations as other microbial infections. Once the symptoms are seen, the doctor will advise a special test called a rapid strep test to detect the bacteria, in which a throat swab is collected and examined in the laboratory.
- A blood test is also carried out to check for infection and to rule out any other major illness.
Treatment:
- The primary treatment of strep throat infections is by antibiotics. It is very important to ensure that a patient does not skip any dose of the antibiotic to eliminate the bacteria completely.
- If pain or fever are present, analgesic and antipyretic medications will also be given.
- There is a risk that strep throat may relapse if the course of the medicine is not completed or the bacteria develop resistance to the medicine.

 OTC Medicines for Strep Throat
OTC Medicines for Strep Throat