While the majority of the patients of COVID-19 infection suffer from mild symptoms of COVID-19 infection such as fever, cough and difficulty breathing, some of the patients also suffer from severe symptoms such as extreme difficulty in breathing, persistent pain in the chest, a state of confusion (delirium) and bluish discolouration of the face and lips. Patients who show these severe symptoms are prone to respiratory complications like viral pneumonia and pulmonary embolism. These people require mechanical ventilation for life support.
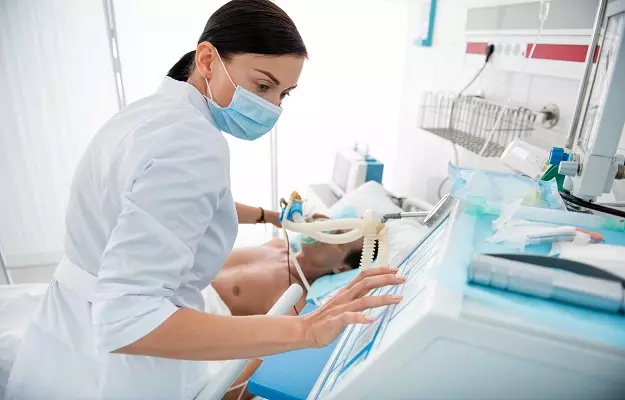
A ventilator is an emergency respiratory machine that is used to provide breathing assistance to a person who cannot breathe on their own. A ventilator doesn't treat their disease or condition but provides oxygen to their lungs and removes carbon dioxide from their body.
There two different types of ventilators that can be used for COVID-19 patients: negative pressure ventilators (non-invasive) and positive pressure ventilators (invasive). In most of the cases, positive pressure ventilators are used for critically ill COVID-19 patients.
A ventilator is a complex machine which requires expertise for its management. The oxygen is delivered to the body of the infected patients with the help of tubes which are inserted in the nose and mouth of the patient.
A nasogastric tube is inserted through the nose which goes till the stomach. This tube is used to deliver food to the patient’s body. Another tube called the endotracheal tube (ET tube) is inserted through the mouth of the patient to their windpipe (trachea) to transport oxygen to the lungs. The other end of the ET tube is attached to the ventilator.
The ventilator transfers oxygen into the ET tube which delivers that oxygen to the lungs. Once the oxygen reaches the patient’s body, the ET tube receives carbon dioxide from the lungs. That is how the cycle continues.
However, people who receive this mechanical ventilation are at an increased risk of getting the complications related to it. Here in this article, we will tell you about the risks of a ventilator in the patients with COVID-19 infection.