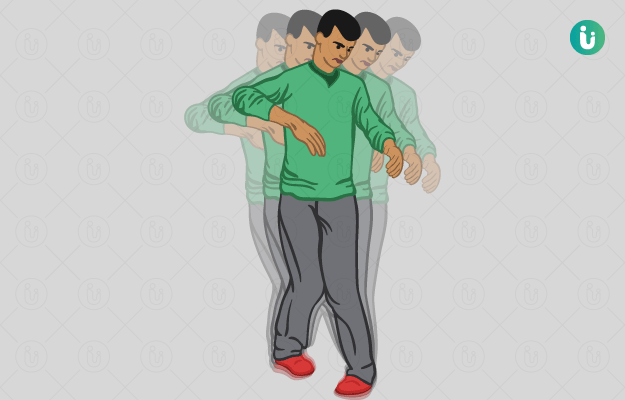
Ataxia is a type of movement disorder marked by lack of coordination in the muscles, which results in loss of control over speech, movement and balance. It is a degenerative neurological condition in which there is damage to the cerebellum, a part of the brain that controls and coordinates movement in the body.
The common signs of ataxia include a general loss of balance and coordination in the body, slurred speech, inability to walk or pick things up, difficulty in making eye movements and a lack of ability to swallow food.
The impairment of several voluntary movements in the body can also be due to damaged nerve cells around the cerebellum, and it can also be passed down by way of faulty genes from parents.
According to the National Ataxia Foundation of the United States, approximately 150,000 people suffer from this rare condition in America, while research suggests that it affects about 16,000 people in Germany.
In studies performed in India, community-based statistics indicate that ataxia is a rare disorder in the country, affecting about one to two people in a population of about 100,000.
Ataxia can be a sign of an underlying condition such as multiple sclerosis (MS), stroke, brain tumour, brain, head or spinal injury or can even be a result of alcoholism. As it is a degenerative condition, ataxia cannot be cured but can be managed through treatment that involves alleviating the symptoms.

 Doctors for Ataxia
Doctors for Ataxia  OTC Medicines for Ataxia
OTC Medicines for Ataxia