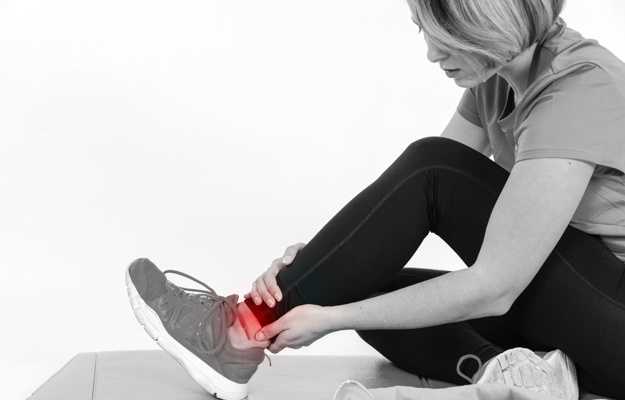
The Achilles tendon is at the back of the heel. It can be ruptured by sudden force on the foot or ankle. If your Achilles tendon is ruptured, you won't be able to stand on tiptoe and will have a flat-footed walk. It is important to diagnose and treat this injury as soon as possible, to help promote healing. Treatment involves wearing a plaster cast or brace (orthosis) for several weeks, and possibly having an operation.
What is the Achilles tendon?
The Achilles tendon is a vital component of the lower limbs. It is present right behind and above the heel area of the body. It helps to join the heel bone to the muscles in the calf. The Achilles tendon performs the function of plantar flexion. Plantar flexion is the movement that helps in bending the foot downwards at the level of the ankle.
What is an Achilles tendon rupture?
When there is a tear in the Achilles tendon, it is defined as an Achilles tendon rupture. This tear may be classified as a partial or complete tear. In the case of a partial tear, the tendon is still attached to the calf muscle. In certain situations, if the tendon is completely torn away, the connection between the ankle bone and the calf muscles is completely lost.
How common is this condition?
It affects around two lakh people a year. It is more commonly observed in people who undertake sports and intense training. People of all ages can experience this rupture but it is most common between the ages of 30 and 50 years old.
Best treatment for Achilles tendon rupture
A lot of research has been done to settle the debate between the two treatment options that are available, i.e., surgical repair or conservative treatment.
Studies suggest that surgical repair has a major advantage in that it helps to decrease the risk of another rupture (re-rupture) of the Achilles tendon in the future. An important disadvantage to consider is the risks of surgery like excessive bleeding or infections. Sometimes, a second surgery may be required if resolution does not occur after the first procedure. Therefore, surgery is the ideal treatment protocol for patients who take part in intense exercise and sports or for people who belong to a younger age group. When surgery is required, percutaneous surgery is performed that allows the surgeon to repair the injury using smaller incisions as compared to a traditional approach. This limits the risk of developing infections at the site of operation.
Conservative management is commonly advised for patients who are not very active, are old or have a blood clotting disorder. It is also used in people who do not wish to undergo surgery. The kind of treatment varies depending on the clinical profile of the patient and the personal choice of the patient. Sometimes, surgery is necessary if there have been some delays in the initiation of treatment for the rupture.
A recent study shows that both treatment protocols gave good results, especially when early mobilisation therapy is achieved with the help of a brace.

 Doctors for Achilles tendon rupture
Doctors for Achilles tendon rupture