The novel coronavirus, COVID-19, is a part of the coronavirus family which affects the respiratory tract of the infected people. First seen in Wuhan, China, COVID-19 has been rapidly spread across the countries. COVID-19 has been declared a pandemic by the World Health Organisation on 11 February, 2020. Since then, it has affected around 195 countries and territories. The count of COVID-19 infected people has gone up to 562 cases in India.
To prevent the further spread of the infection, on 24 March 2020, the Prime Minister of India announced a complete lockdown for 21 days across the country. People are urged to stay at home, and those who have returned from recent foreign travel are being asked to self-quarantine themselves for 14 days to prevent the spread of the infection.
In this article, you will read about the ways of spreading of COVID-19 infection and the high-touch surfaces that can act as a medium for the virus transmission.
- How does COVID-19 spread?
- Types of human to human transmission
- What are the high-touch surfaces and fomites?
- What can be done to clean the high-touch surfaces and fomites?
How does COVID-19 spread?
COVID-19 is a contagious infection and it can spread in various ways, such as:
1. Through person to person contact
The COVID-19 infection can spread through direct human contact. That means the infection can spread directly if a healthy person comes in contact with the infected person. When an infected person sneezes or coughs, they contaminate the air-particles around them. If these infected air-particles are inhaled by a healthy individual, the virus in the air enters their body through mouth, nose and eyes.
2. Through contaminated surfaces
The COVID-19 infection can also spread through indirect contact, that means without touching or coming near the infected person. An infected person can spread the virus-containing droplets on the surrounding objects and surfaces on sneezing and coughing. When a healthy person unknowingly touches these surfaces, the virus sticks to the surface of their hands. The virus enters into the body of the healthy person through different portals as they touch their eyes, nose and mouth with the same unwashed hands.
3. Through community spread
If a person in a community is infected with COVID-19 but is unaware of how and where they got infected, they can spread the virus rapidly and sustainably in that community. This is known as community spread.
Types of human to human transmission
Data show that COVID-19 patients start showing symptoms between one day and 14 days after catching the infection - the lag between being exposed to the virus and showing symptoms is known as the incubation period. The median incubation period - based on available data - is five to six days. That said, 80% of patients get a mild or asymptomatic case of COVID-19.
COVID-19 is highly contagious - a healthy person can also get the disease via direct contact with someone who is infected but doesn't show any symptoms. In its "Situation Report 73" of 2 April 2020, WHO underlined these three modes of human-to-human transmission:
- Symptomatic transmission: When a healthy person gets this infection by coming in contact with someone who has COVID-19 symptoms like fever, cough and shortness of breath, this is known as symptomatic transmission.
According to the WHO report, patients may be more contagious in the early stages of the disease when their symptoms are just starting to show. "That is, within the first 3 days from onset of symptoms," the report says. - Pre-symptomatic transmission: When a healthy person gets the infection from someone who isn't showing symptoms yet, it is known as pre-symptomatic transmission. This could occur during the incubation period of 1-14 days.
- Asymptomatic transmission: Catching the infection from a COVID-19 patient who has been confirmed sick by the COVID-19 (SARS-CoV-2) test in a lab but doesn't show symptoms is known as asymptomatic transmission.
The WHO report adds: "There are few reports of laboratory-confirmed cases who are truly asymptomatic, and to date, there has been no documented asymptomatic transmission. This does not exclude the possibility that it may occur."
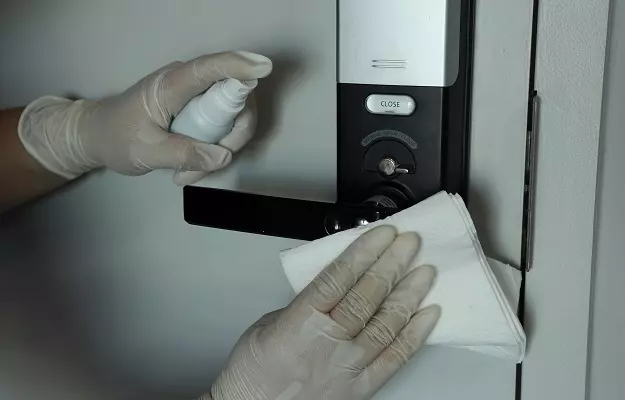
What are the high-touch surfaces and fomites?
During or after an illness, viruses are scattered in large numbers in different body secretions like blood, faeces, urine, saliva, and nasal fluid. In the case of COVID-19, the nasal and oral secretions (droplets from coughing and sneezing) are the medium of virus transmission. The scientists are not sure but they believe that the COVID-19 virus can stay on non-living surfaces for hours to days.
Healthcare professionals have been advising people to clean and disinfect high-touch surfaces and fomites as they can act as a carrier for the virus.
The most common high touch surfaces are:
- Doorknobs
- Light switches
- Phones
- Remotes
- Sink faucets
- Elevator buttons
- Tabletops
- Cabinet pulls
- Laptop keyboard
- Kids’ toys
Fomites are inanimate objects which can get infected easily and have the potential to become a vehicle to spread the infection to a healthy person through indirect contact. Fomites can get contaminated with the virus by coming in direct contact with the body fluids, infected hands, sneezing or coughing. Your blanket, soft toys, bowls, buckets, clippers and clothing are an example of fomites.
What can be done to clean the high-touch surfaces and fomites?
People are being asked to stay clean and keep their surroundings free of germs in order to prevent the spread of COVID-19 infection. Studies have depicted that disinfection of fomites reduces surface contamination and interrupts the spread of viral diseases.
These are the following ways in which you can clean and disinfect the high-touch surfaces and fomites:
- You should clean the frequently touched surfaces with either a reusable cloth or a disposable towel dipped in a disinfectant, cleaning agent (or detergent) and warm water. You can wear gloves while cleaning these surfaces. Make sure that you remove all the dirt and soil from the surface.
- If possible, use disposable towels for cleaning. If you are using reusable cloths, scrub them properly in hot water after cleaning.
- Do not keep the soiled clothes back in the closet which you would have worn while going outdoors. You should launder these clothes with detergent and a clear disinfectant.
- You can use commercially available disinfecting wipes to clean the electronic devices like remotes, laptop keyboards and light switches. Do not use the same wipe again and again for the same device.
To protect your child from the viral infection, sanitize and clean their toys as much as possible. You can clean your kids’ toys by following ways:
- If your child has a chew toy, make sure that you sanitize the toy in boiling water or air-dry it to clean all the surfaces.
- For the toys that can be soaked, pour any disinfecting solution in a large basin or sink and soak the toys in it for at least five minutes. Scrub the toys vigorously to remove all visible debris from the surface of the toys. You can dry the toys in the dryer on the high heat setting for better disinfection.
- For the toys that cannot be soaked in the disinfecting solution, clean these toys with either a disinfecting wipe or cloths dipped in a disinfecting solution. Make sure that the surfaces remain wet for at least 5 minutes to achieve complete sanitization.
Doctors for How does COVID-19 spread

Dr Rahul Gam
Infectious Disease
8 Years of Experience

Dr. Arun R
Infectious Disease
5 Years of Experience

Dr. Neha Gupta
Infectious Disease
16 Years of Experience

Dr. Anupama Kumar
Infectious Disease
Medicines / Products that contain How does COVID-19 spread
- Proctosedyl BD Cream - ₹108
- Anovate Cream - ₹140
- Pilo GO Cream - ₹80
- Covifor Injection - ₹3780
- Fabiflu 200 Mg Tablet - ₹1292
- Fabiflu 400 Tablet - ₹856
- Fabiflu (Favipiravir) 400 Mg Tablet - ₹1224
- Fabiflu (Favipiravir) 200 Mg Tablet - ₹1292
- Remdesivir Injection - ₹10500
- Molusafe Capsule - ₹457
- Movfor 200 Mg Capsule - ₹2490
- Molflu 200 Mg Capsule - ₹1400
- Molulife 200 Capsule - ₹1399
- Cipmolnu 200 Mg Capsule - ₹2000
- Molxvir 200 Mg Capsule - ₹1520
- Immunocin Alpha Plus 1.6mg Injection - ₹5998
- Alzumab Injection - ₹8229
- Imualfa 1.6mg Injection 1ml - ₹2628
- Molnutor 200 Mg Capsule - ₹2000
- Sotrovimab Injection - ₹165000
- Nirmatrelvir - ₹5000
- Molnupiravir 200 Mg Capsule - ₹1400
- Covihalt 200 Tablet - ₹465
- Ciplenza Tablet - ₹646
- Itolizumab Injection - ₹8220
References
- Center for Disease Control and Prevention [internet], Atlanta (GA): US Department of Health and Human Services; How Coronavirus Spreads
- World Health Organization [Internet]. Geneva (SUI): World Health Organization; Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) technical guidance: Infection prevention and control / WASH
- American Society for Microbiology [Internet] NW Washington, DC; Significance of Fomites in the Spread of Respiratory and Enteric Viral Disease.
- Department of Food, Nutrition, and Packaging Sciences [Internet]. Clemson University. Clemson. SC. United States; Cleaning and Disinfecting High-Touch Surfaces ,